 Rail transport in Europe is more important to military planners because military equipment is predominant and the rail network is extensive in the region. Korea also has a standard-gauge rail network. The three railclearance diagrams or envelopes of greatest interest are the Gabarit International de Chargement (GIC), NATO Envelope M, and the Korean clearance diagram.
Rail transport in Europe is more important to military planners because military equipment is predominant and the rail network is extensive in the region. Korea also has a standard-gauge rail network. The three railclearance diagrams or envelopes of greatest interest are the Gabarit International de Chargement (GIC), NATO Envelope M, and the Korean clearance diagram.
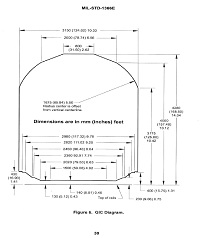
The GIC applies to rail lines in Europe. Equipment that is mounted on 51.4-inch high railcars and is within the limitations of the GIC diagram or envelope will be capable of essentially unrestricted movement worldwide on standard-gauge rail lines.
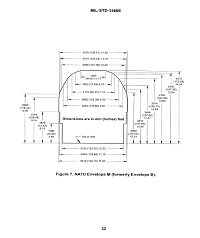
Envelope M applies to rail lines in NATO countries on the European continent. Envelope M provides for preplanning for rail movement of equipment exceeding the GIC. Measurements and equipment sketches are completed before the first rail movement to support planning for future movement. The equipment Envelope M rail network is not as extensive as the GIC equipment network. If equipment exceeds Envelope M, it may require special routing and provisions. This may result in deployment delays during crisis contingencies. This may result in deployment delays during crisis contingencies.
STANAG 2175 that used to define ordinary and exceptional rail transport has been withdrawn and has been replaced with AMovP-4(A) - The Technical Aspects of the Transport of Military Materials by Railroad. This document was developed to provide one allied publication to document the procedure and all technical rules applicable to loading/unloading and transport of military equipment on railway wagons.
 Military vehicles for rail transport in Allied NATO countries must consider the following:
Military vehicles for rail transport in Allied NATO countries must consider the following:
- The size and capacity of the flat wagons.
- The axle or bogie load distribution of the wagon, its ratio cannot exceed 2/1 for a non-bogie wagon, and 3/1 for a bogie wagon in the longitudinal direction while staying under the maximum load per axle. The ratio of 10/8 must also not be exceeded in the lateral direction between the wheels of a same axle.
- The width of the equipment. The usable loading width determines the supporting width of the equipment. If it is tracked equipment on double rollers, the outer half of each track must be for at least 65mm on the wagon floor. If it is tracked equipment on single rollers, its tracks must be for at least 2/3 + 15mm of its width on the wagon floor. Tires of wheeled vehicles must in principle stand completely on the wagon floor.
- Fitting within Loading gauges/envelopes. The loaded flat wagon must definitely fit inside the loading gauge or envelope as defined by the Forces.
Items of equipment that do not meet GIC diagram clearances may still be transported on the major NATO rail lines provided they meet Envelope M.
The Korean clearance diagram applies to the rail line in the Republic of Korea (ROK), also known as South Korea. As with Envelope M, equipment exceeding the diagram may require special routing and provisions resulting in deployment delays.