Markings
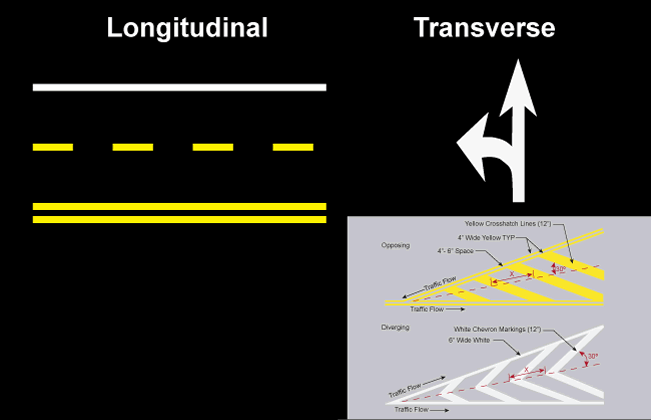
Markings on roadways provide continuous guidance and information for the motorist. Pavement markings may be categorized into two primary groups: longitudinal markings and transverse markings. Longitudinal markings help facilitate vehicle guidance and location while transverse markings provide warning and regulatory information to the motorist. Both types of pavement markings provide vital information to the vehicle operator, and as such must be uniform in design, position, and application.


Markings MUST be uniform so they can be recognized and understood instantly by all drivers. The MUTCD provides the basic principles and meanings to which all pavement markings should adhere. Further information is presented in SDDCTEA Pamphlet 55-14. Also, see SDDCTEA’s DOD MUTCD Supplement.
Marking durability is affected by material characteristics, traffic volumes, weather, and location. There are various types of pavement marking materials including paint, thermoplastic, preformed plastic, and epoxy.
When selecting a material type, consider a balance between cost and performance longevity. Most installations utilize paint as it is a low-cost marking material. On average, the expectancy of paint is approximately two years. Pavement markings should be inspected annually to ensure they are in acceptable condition and provide the specified color throughout their useful life. Additionally, markings that are no longer applicable for roadway conditions or restrictions and that might cause confusion for the road user shall be removed or obliterated to be unidentifiable as a marking as soon as practical. Pavement markings have limitations. The visibility of markings can be limited by snow, debris, and water.