Acceptable Types of Barrier Systems
Roadside barriers are typically categorized as flexible, semi-rigid, or rigid; depending on their deflection characteristics resulting from an impact from a vehicle.
Flexible Systems

Flexible barriers, including the W-beam weak post system, are the most forgiving barriers because they deflect on impact. Barrier deflection lessens vehicle impact forces and contains the vehicle, rather than redirecting it. However, flexible barriers require large lateral clearances.
Semi-Rigid Systems

Semi-rigid barriers, including the blocked out W-beam (Strong Post) system, are less forgiving than flexible systems because they exert higher forces on the vehicle. Semi-rigid barriers redirect vehicles rather than contain them. Installations include timber or plastic composite blockouts. These blockouts minimize vehicle snagging on the posts and reduce the likelihood of a vehicle vaulting over the barrier.
The strong-post W-beam is the most common barrier system in use today. It consists of wood posts and wood blockouts or steel posts that support a W-beam rail element blocked out from the posts with routed timber or composite blockouts.
Rigid Systems (Concrete and Masonry)
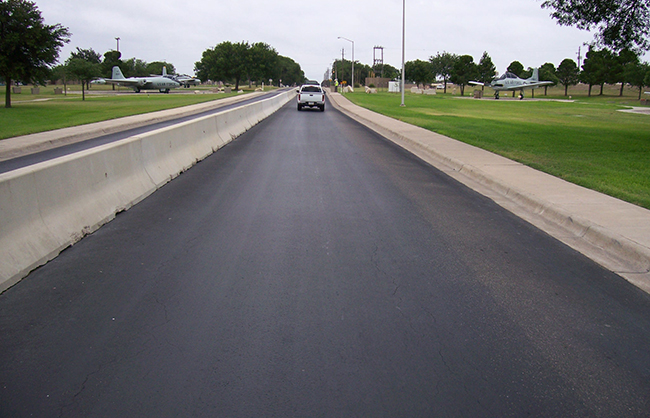

Rigid barriers, including the New Jersey Safety-Shape barrier and F-shape barrier, have positive and negative aspects. On the positive side, they have no barrier deflection. On the negative side, they exert large impact forces on vehicles. They are recommended for construction projects, in areas without medians, and where little or no deflection is permitted.
In summary, refer to the AASHTO MASH for approved systems and their associated test level. As the list covers the most widely used barriers, it is not intended to be all-inclusive. As an additional source and as a general practice, consult your state highway agency's standards for barrier systems that have been crash tested and approved, and would be standardized with other barrier installations in your area. Note that preapproved NCHRP Report 350 products may still be used.